观察网站
查看源代码只有网站外观设计后,发现F12抓包后名为[practice]的文件内有“label”和”questionBh”两个题目号
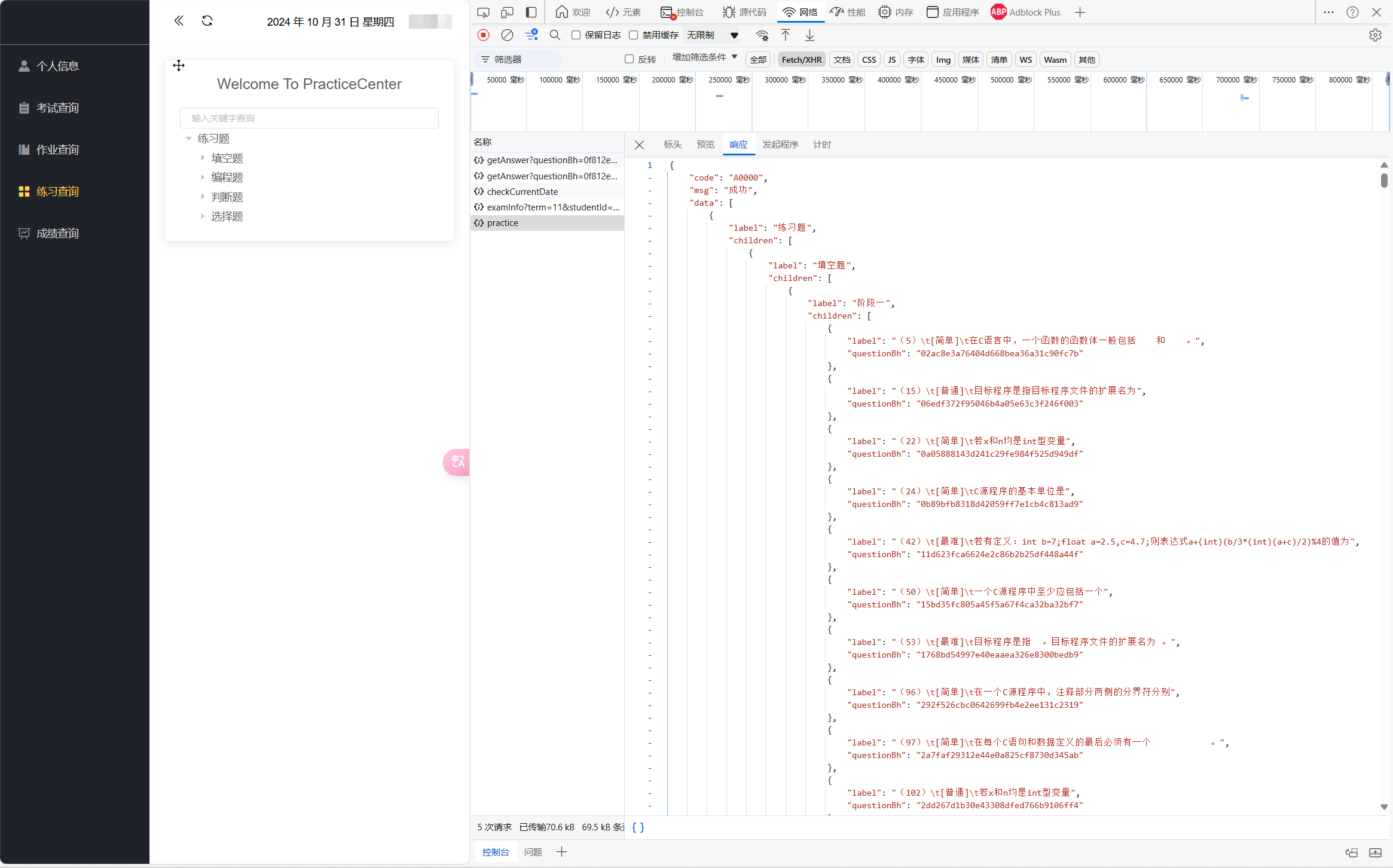
点进题目后再点击查看答案,抓包的文件”data”中就有完整的答案
![点进一道题目,并点击参考答案]/images/(3.png)
点开第二次抓包的标头,发现url是http://[一些域名]={questionBh}
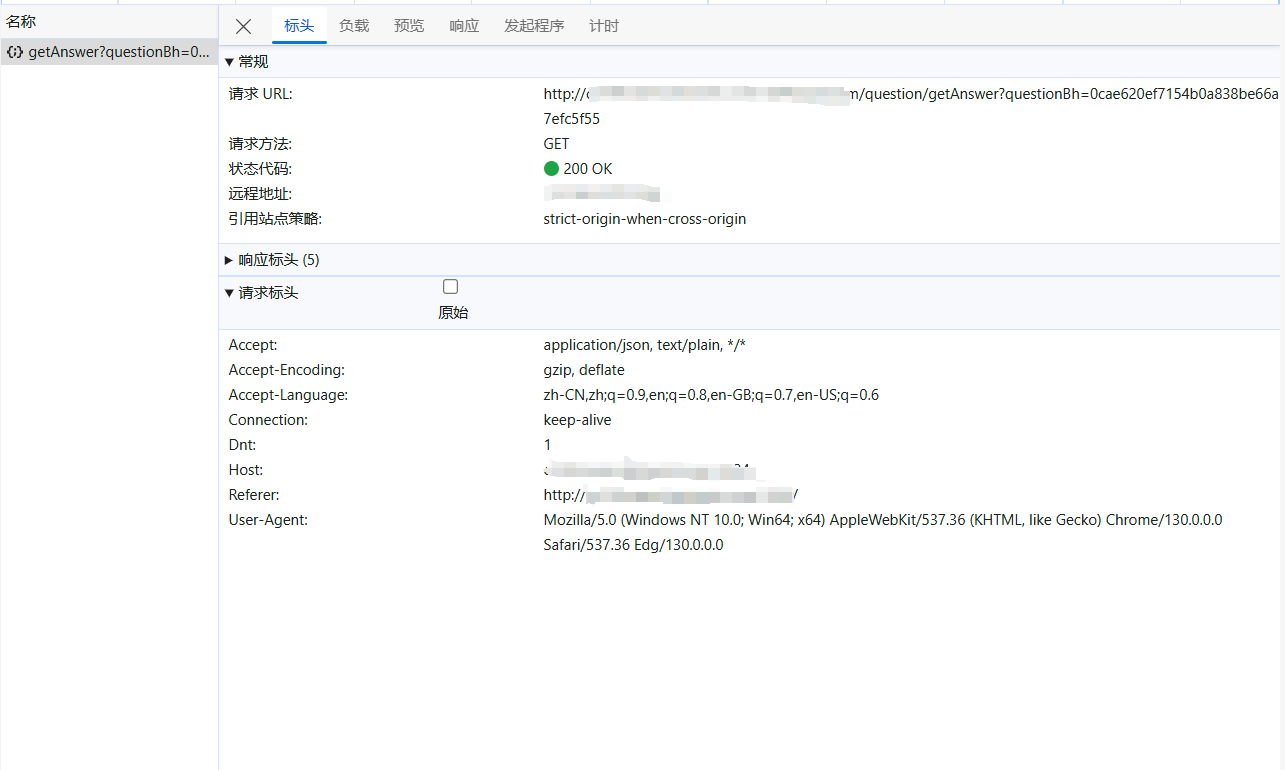
我们可以通过 label -> questionBh -> answer
写代码
先进行 label -> questionBh 的步骤
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| import requests
import re
import csv
url = f'http://[一些域名]/api/exam/question/practice'
headers = {
"user-agent":"Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/130.0.0.0 Safari/537.36 Edg/130.0.0.0"
}
resp = requests.get(url,headers=headers)
obj = re.compile(r'"label":"((?P<num>.*?))(?P<none>.*?)questionBh":"(?P<web>.*?)"',re.S)
result = obj.finditer(resp.text)
for i in result:
print(i.group("num","web"))
resp.close()
|
再对得到的格式进行一些调整,并变成csv格式,示例如下
1
2
3
| num,questionBh
5,02ac8e3a76404d668bea36a31c90fc7b
*,********************************
|
再进行 questionBh -> answer 的步骤
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| import requests
import re
import csv
query= input("输入你想搜索的东西\n")
url = f'http://[一些域名]/api/exam/question/getAnswer?questionBh={query}&studentId=2024011666'
headers = {
"user-agent":"Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/130.0.0.0 Safari/537.36 Edg/130.0.0.0"
}
resp = requests.get(url,headers=headers)
obj = re.compile(r'"data":"(?P<ans>.*?)"}',re.S)
result = obj.finditer(resp.text)
|
整合代码,通过csv文件串联起来
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
| import csv
import requests
import re
def load_mapping(file_path):
mapping = {}
with open(file_path, mode='r', encoding='utf-16be') as file:
reader = csv.reader(file)
next(reader)
for row in reader:
num, questionBh = row
mapping[num] = questionBh
return mapping
def get_question_bh(num, mapping):
return mapping.get(num, "Not Found")
file_path = 'mapping.csv'
k = input("输入题号:")
mapping = load_mapping(file_path)
question_bh = get_question_bh(k, mapping)
print(f"生成的 questionBh: {question_bh}")
k = f"{question_bh}"
url = f'http://[一些域名]/api/exam/question/getAnswer?questionBh={k}'
headers = {
"user-agent":"Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/130.0.0.0 Safari/537.36 Edg/130.0.0.0"
}
resp = requests.get(url,headers=headers)
obj = re.compile(r'"data":"(?P<ans>.*?)"}',re.S)
result = obj.finditer(resp.text)
|
使用 ast 解析转义字符
笔者在学习中发现,使用 ast.literal_eval() 解析转义字符可以消除多余字符的影响,省去了复制到ai转换的麻烦
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| ans_list = [i.group("ans") for i in result]
a = ''.join(ans_list)
escaped_text = ast.literal_eval(f'"""{a}"""')
print(escaped_text)
resp.close()
|
完整代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
| import csv
import requests
import re
import ast
def load_mapping(file_path):
mapping = {}
with open(file_path, mode='r', encoding='utf-16be') as file:
reader = csv.reader(file)
next(reader)
for row in reader:
num, questionBh = row
mapping[num] = questionBh
return mapping
def get_question_bh(num, mapping):
return mapping.get(num, "Not Found")
file_path = 'mapping.csv'
k = input("输入题号:")
mapping = load_mapping(file_path)
question_bh = get_question_bh(k, mapping)
print(f"生成的 questionBh: {question_bh}")
k = f"{question_bh}"
url = f'http://[一些域名]//api/exam/question/getAnswer?questionBh={k}'
headers = {
"user-agent":"Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/130.0.0.0 Safari/537.36 Edg/130.0.0.0"
}
resp = requests.get(url,headers=headers)
obj = re.compile(r'"data":"(?P<ans>.*?)"}',re.S)
result = obj.finditer(resp.text)
ans_list = [i.group("ans") for i in result]
a = ''.join(ans_list)
escaped_text = ast.literal_eval(f'"""{a}"""')
print(escaped_text)
resp.close()
|
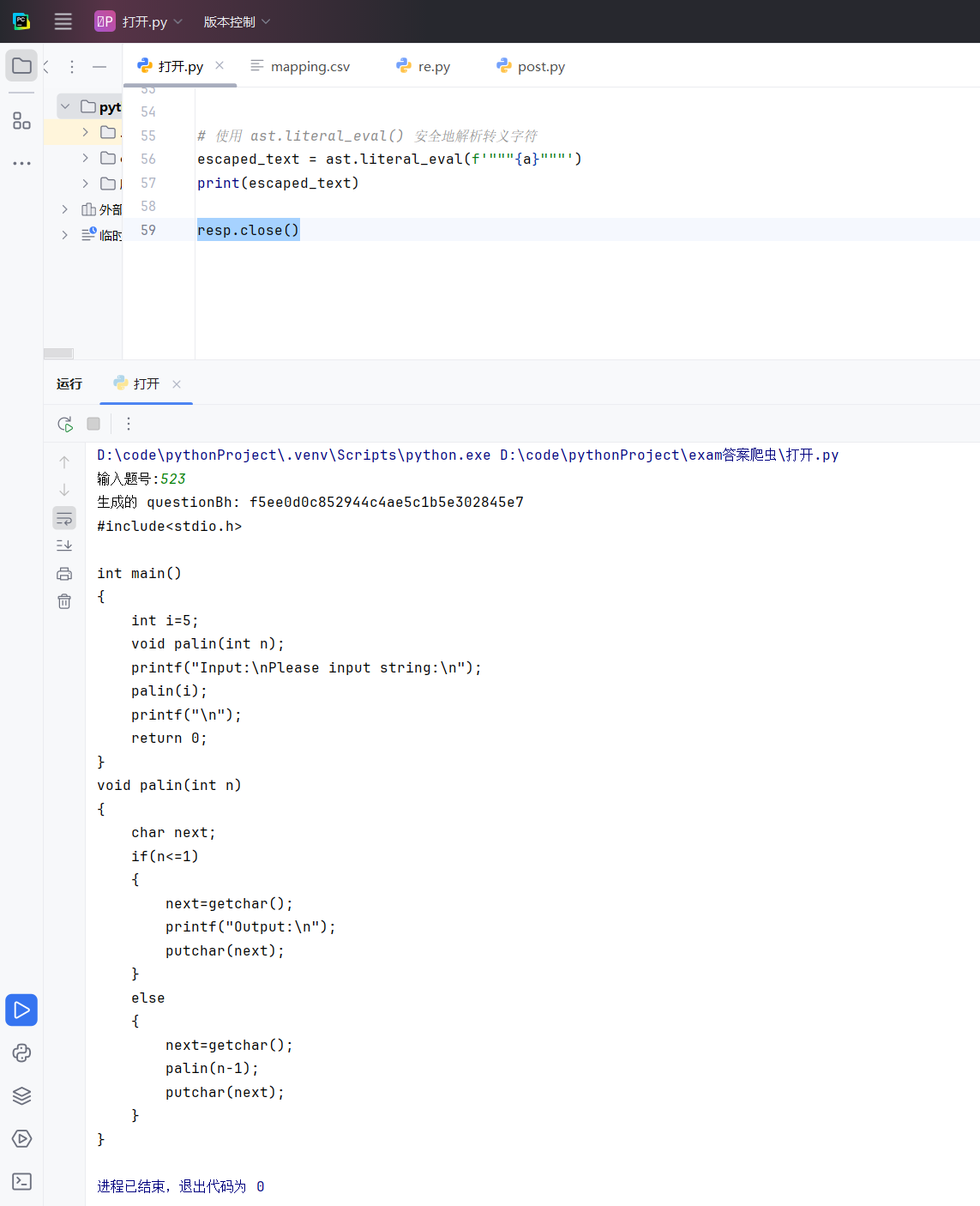
结果
生成结果如下图,经过修改后可以直接复制到提交窗口使用啦
参考
[bilibili]Python爬虫教程 通过视频,我学习了抓包方法,re,正则表达式,最简单的通信原理
在线正则表达式测试


